Public Key Encryption
Ungraded Quiz
-
Can you draw a diagram for hybrid encryption?
-
Can you show cryptographic notation for the diagram?
Key Concepts
Public Key Cryptography
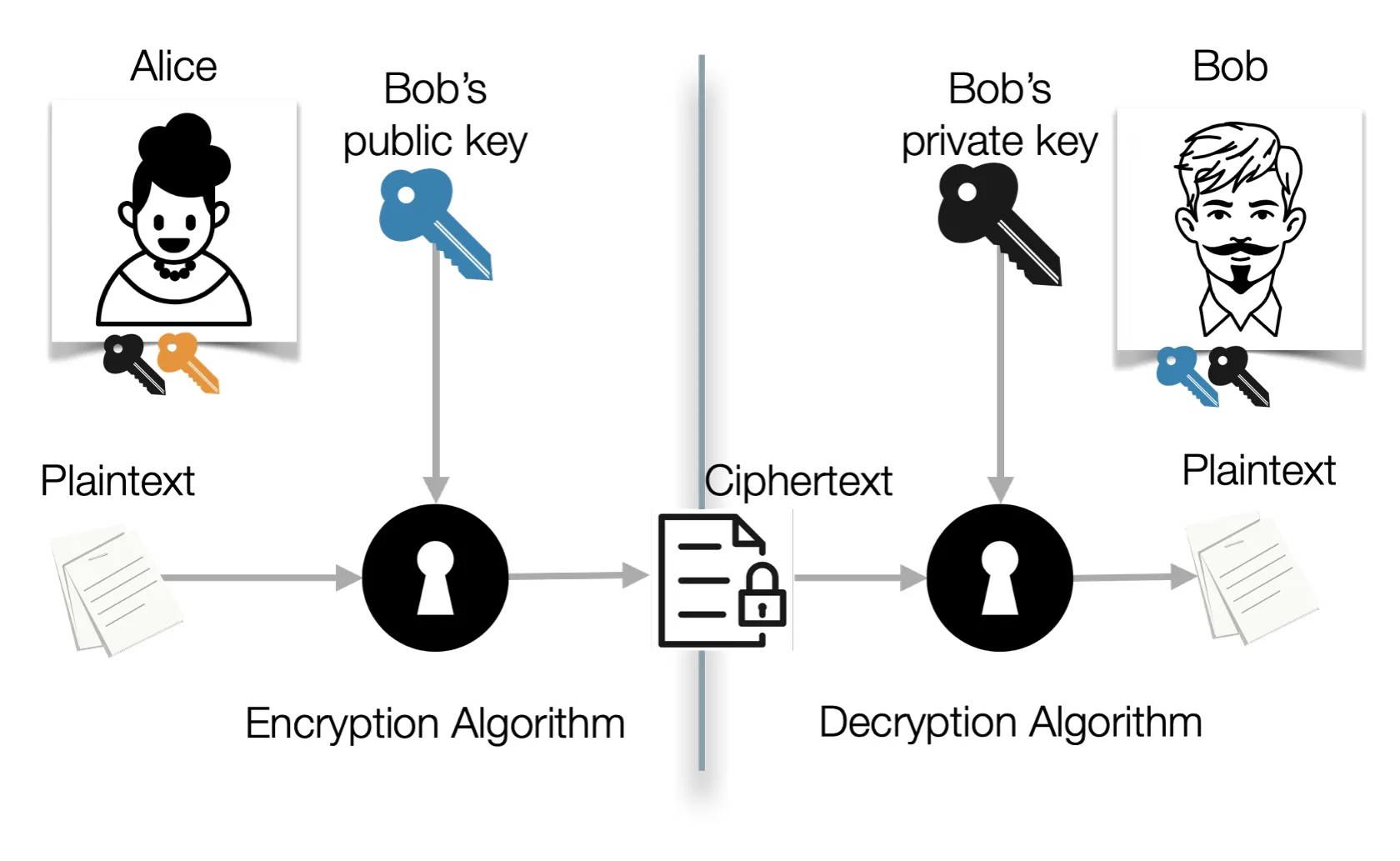
- Each party creates a separate key pair, (public key, private key).
- If Alice knows Bob’s public key, she can encrypt a message using his public
key (eB) and only Bob can decrypt the message using his private key
(dB).
- c = EeB(m)
- m = DdB(c)
- Bob must keep his private key secret, otherwise anybody could decrypt his messages.
- Standard public key cryptography algorithm is called RSA — provides computational security
- Typically use padding with RSA to turn a deterministic encryption into one that incorporates some randomness. A common standard is PKCS#1 v2.
Hybrid Encryption
- Usually, we use public key cryptography to bootstrap a shared, symmetric key.
- This is because encrypting and decrypting with a symmetric key is much fater than encrypting and decrypting with public key cryptography.
- Alice can choose a symmetric key, then encrypt it with Bob’s public key and send it to him. Now they both have a symmetric key they can use to encrypt and decrypt messages to each other.
- See Figure 2.8, page 38
- Alice and Bob can choose a new symmetric key each time they communicate, so we call this a session key.
Digital Signatures
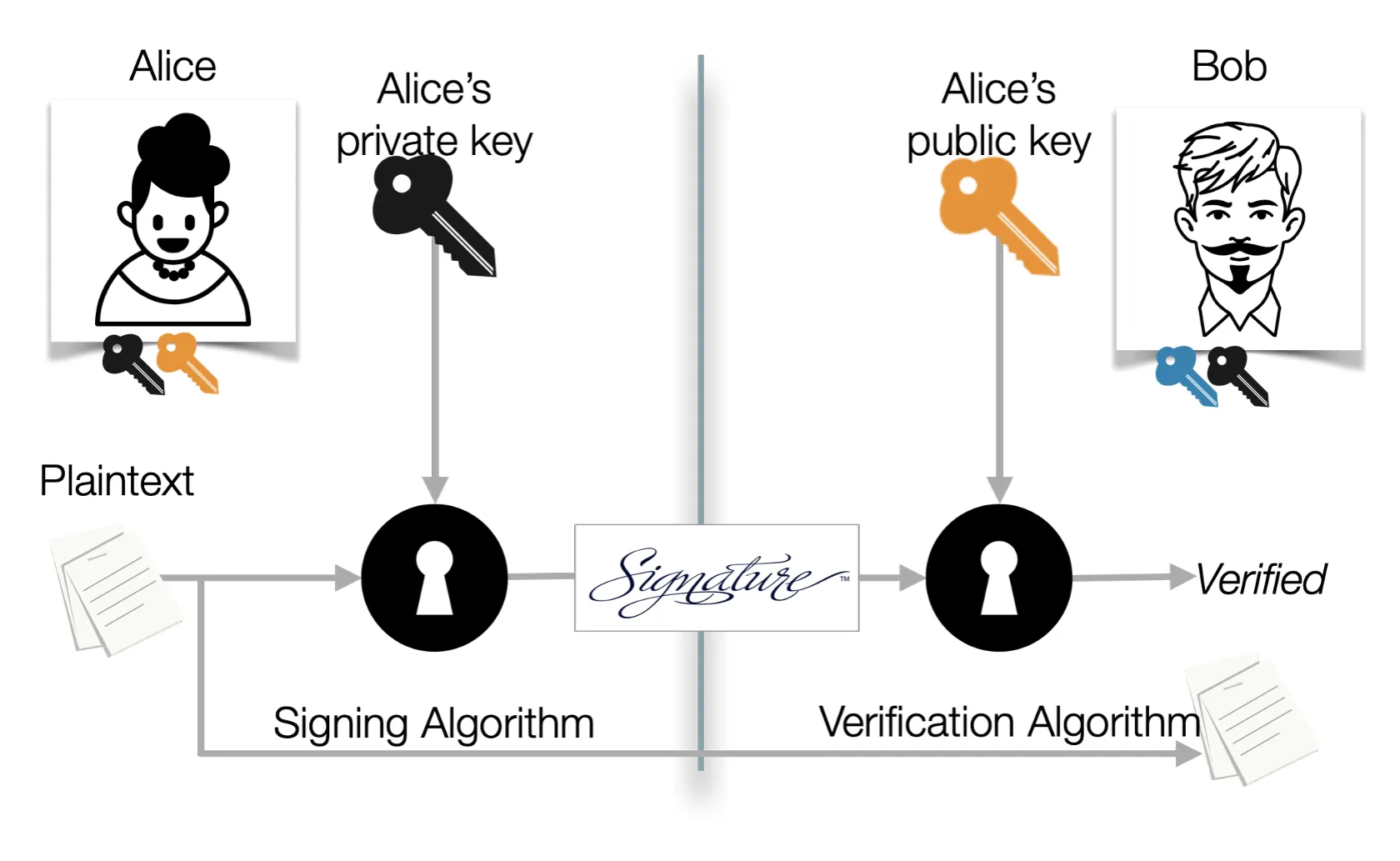
-
Alice can sign (encrypt) a message with her private key (sA). Bob can verify (decrypt) the message with Alice’s public key (vA).
- Here we use (v, s) to represent the (public key, private key).
- Be sure to use separate keys for encryption/decryption and signing/verifying. signing/verifying.
-
Digital signatures provide:
- data origin authentication — we can verify who signed the message
- data integrity — we can verify whether the message is the same as what was signed
- non repudiation — the signer can’t claim they didn’t sign the message (unless someone stole their private key)
-
Use of public key cryptography by the general public is hard because it requires you to keep your private key safe and to have a reliable way to distribute your public key to others. These are key management issues.
Exercise
- Draw a diagram that illustrates how to use hybrid encryption and digital signatures to send a signed message from Alice to Bob. - Should you sign-and-encrypt or encrypt-and-sign? - See Defective Sign & Encrypt in S/MIME, PKCS#7, MOSS, PEM, PGP, and XML