Entity Authentication
Key Concepts
Entity Authentication
-
Alice and Bob share a key in advance
-
Later, how can each side prove that they know the key? For example, if they want to prove they really are talking to each other
-
A simple method is to use a challenge-response protocol
- Alice sends a challenge that Bob can only answer if he knows the secret
- Such a protocol is called a proof of knowledge protocol
-
Unilateral: Alice wants Bob to prove he has the secret
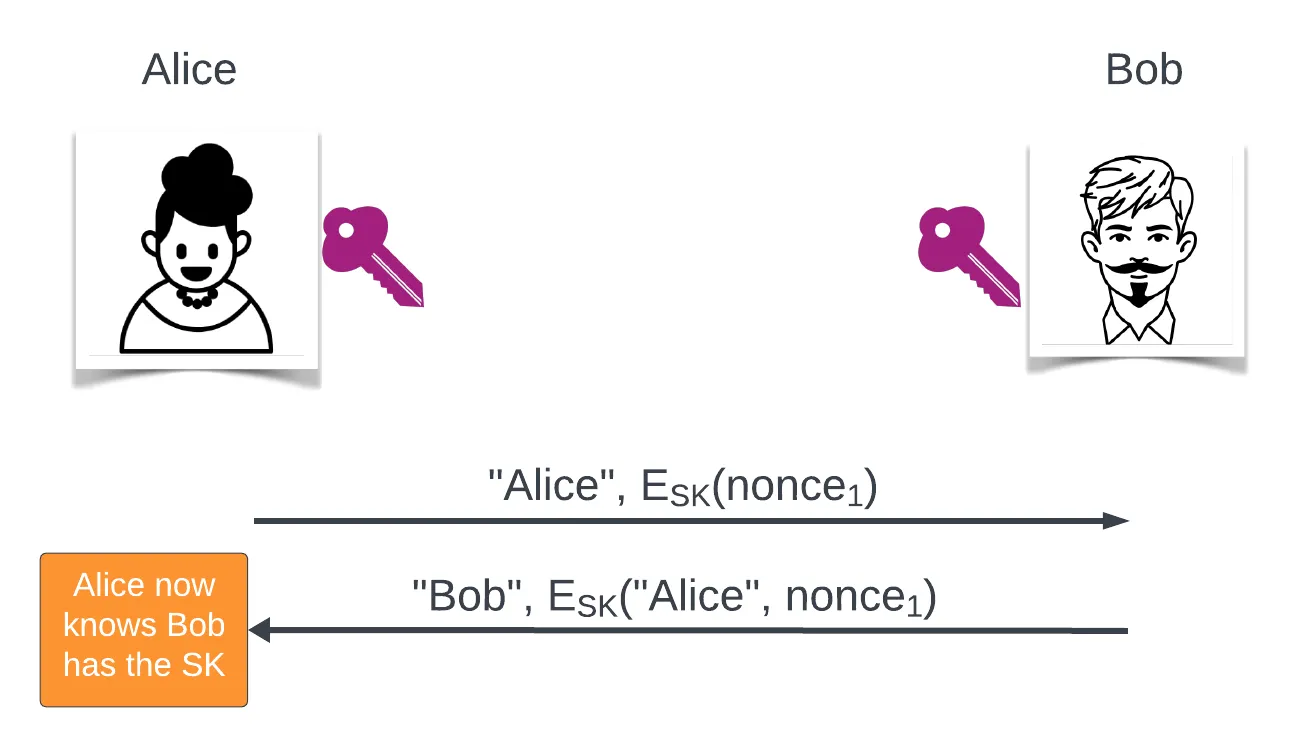
- Mutual: Alice and Bob prove to each other they have the secret
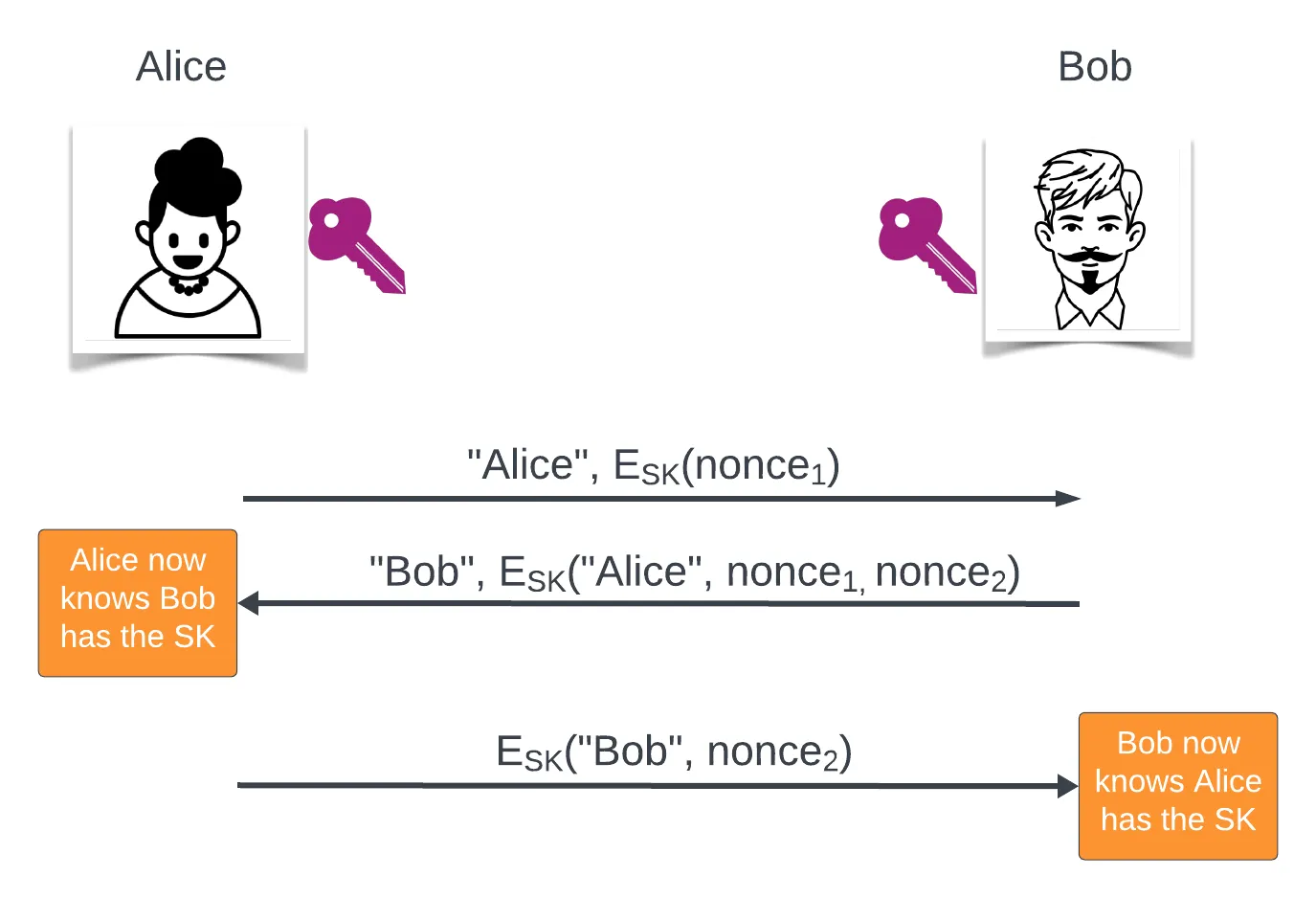
Key Establishment
- How do Alice and Bob establish the secret key in the first place?
- Usually want to establish a session key, meaning a new key for each time you
talk
- key transport: one key chooses the key and needs to get it to the other party
- key establishment: derive a shared key using information from both parties
- Generally want to authenticate the other party AND establish a session key all at once
- Key management is hard
- establishing shared keys
- securing them in transit and storage