SSH, VPNs, and IPSec
Questions on the readings
The readings today are from Computer Security and the Internet, Chapter 10, sections 10.3 - 10.5.
SSH
- provides an encrypted tunnel between two hosts
- typically, we think of a tunnel as a way to connect two machines over a network that doesn’t support the service we want
- in this case, ssh provides an
encrypted connectionfor remote access, over an unencrypted network
- we used to have cleartext utilities for working with remote hosts, and now there are encrypted equivalents:
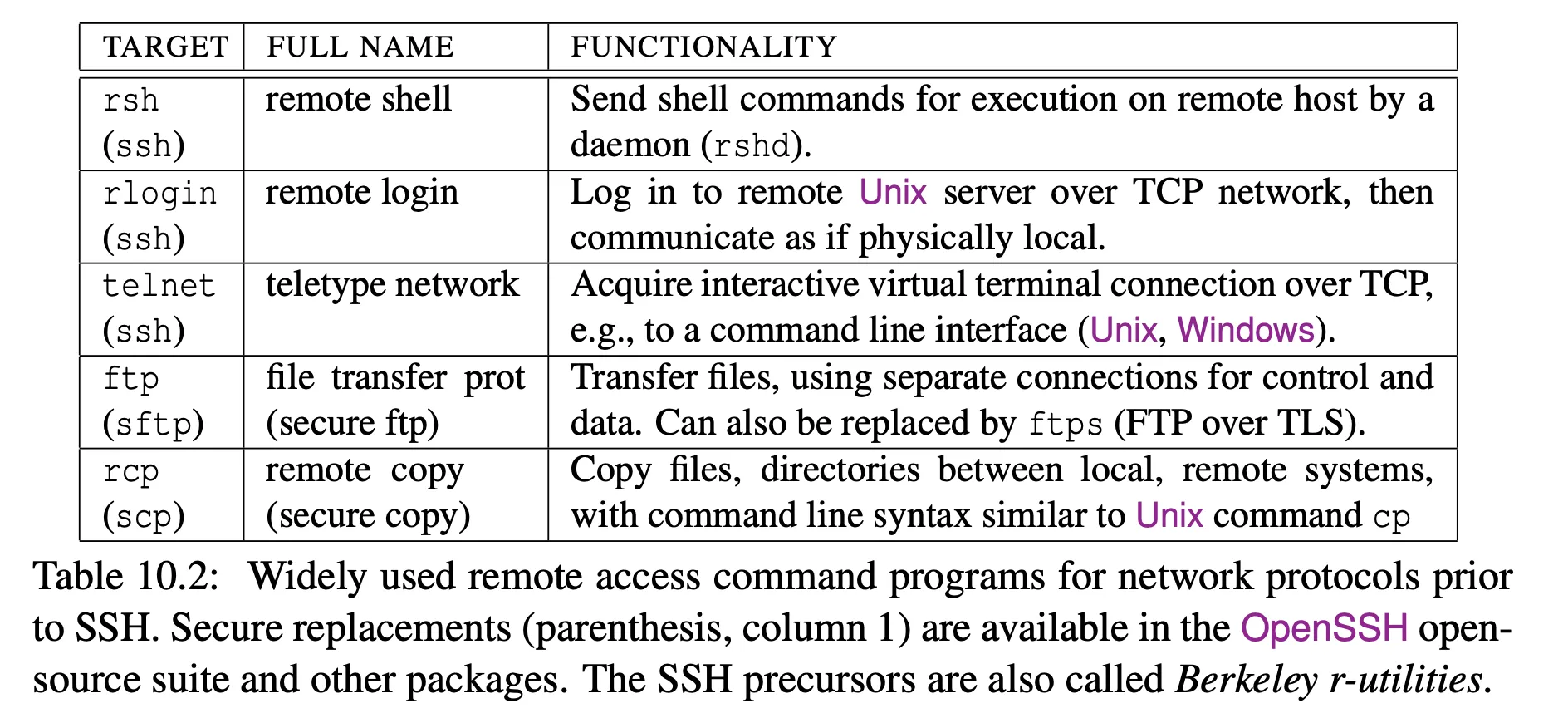
- high level overview of ssh:
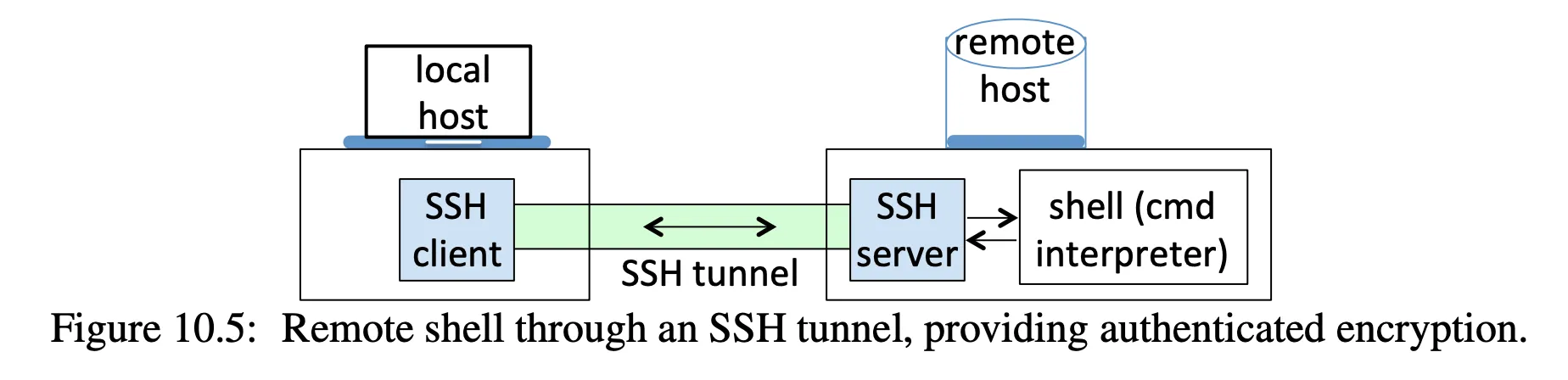
-
protocols
- transport protocol: authentication, encryption, integrity, negotiates parameters and keys
- user authentication protocol: handles user authentication, runs on top of the transport protocol
- connection protocol: enables multiple logical connections over a single physical connection, also runs over the transprt protocol
-
user authentication
- password
- Kerberos ticket
- client public key
-
public key authentication
- client sends public key and signature over data, including session ID
- public key must be pre-registered as an authorized key
- signature must be valid
- session data must match
- you should set up public key authentication when you use ssh and you should put a password on your private key
-
SSH server authentication
- outside of busineses, we often use TOFU (trust on first use) for a server
key
- can verify a hash of the fingerprint if you can get a valid hash over an independent channel — not done in practice
- in enterprises, use a CA model, with a CA managed by the enterprise
- outside of busineses, we often use TOFU (trust on first use) for a server
key
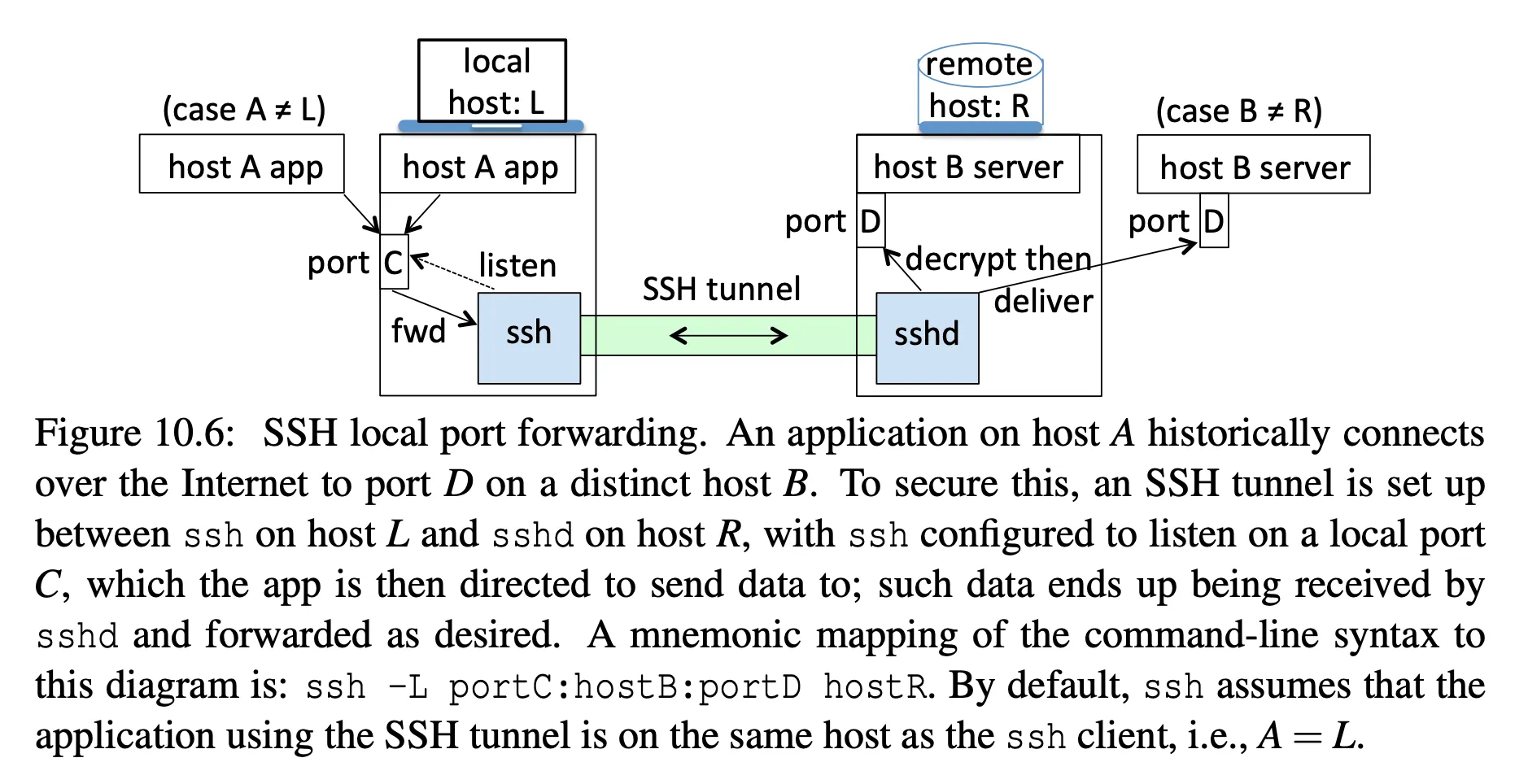
-
you are used to using
sshto manually make a connection, but it can also be set up as a tunnel:- forward all traffic going to specific local port to a remote host and port
- e.g. send all traffic destined for port 2000 on my machine to a remote machine port 25 (email)
- benefit: traffic is encrypted while it is in transit
- benefit: the applications on the local and remote host do not need to be “ssh-aware”
-
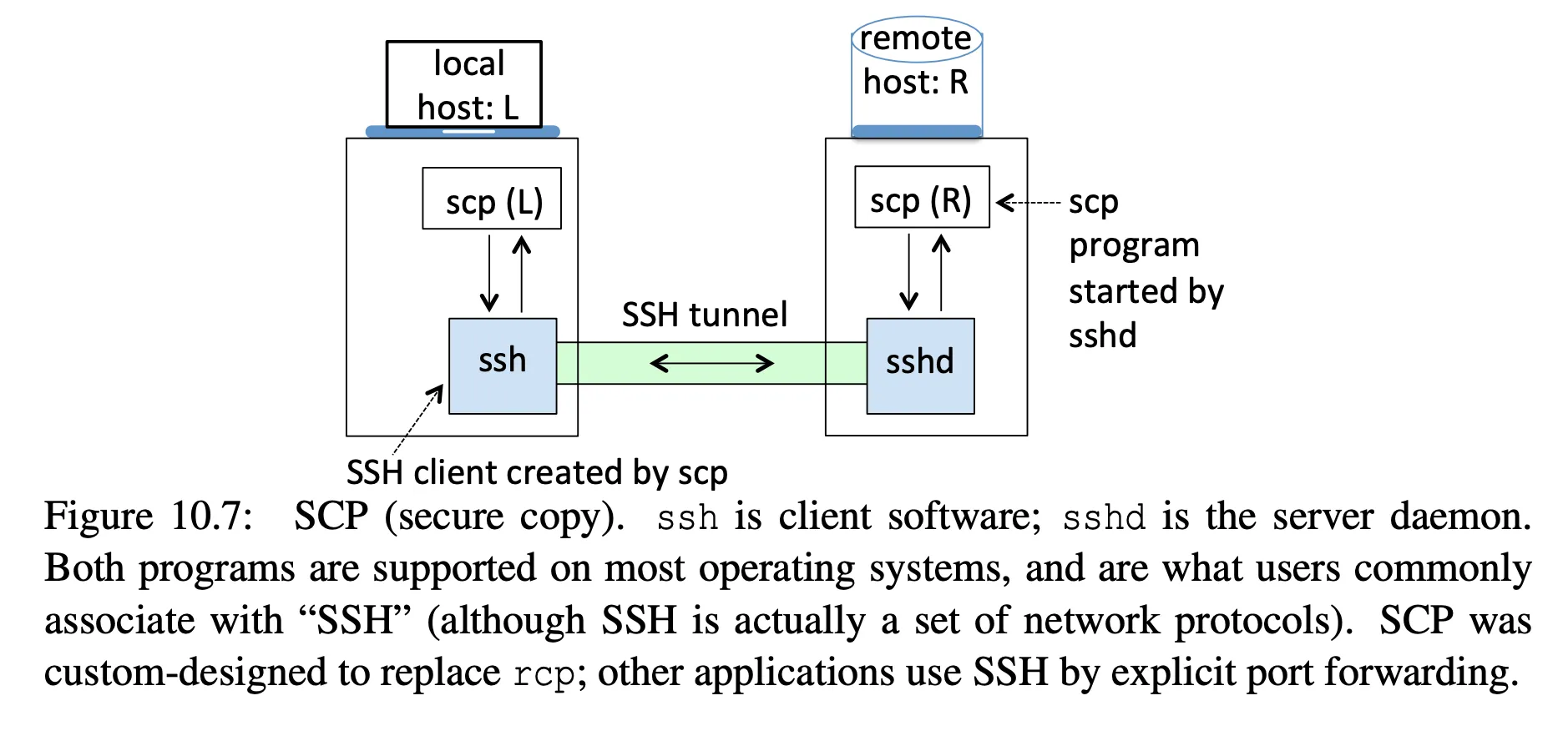
How scp works:
- old model of trusted logins illustrates the dangers of transited trust
- used to have a file of trusted hosts in
/etc/hosts.equiv - if you are authenticated as a user on a trusted host, you can log into this machine as that same user with no authentication!
- used to have a file of trusted hosts in
VPNs
-
Virtual Private Network
-
want to extend a private network (home or enterprise) to other locations with an encrypted tunnel:
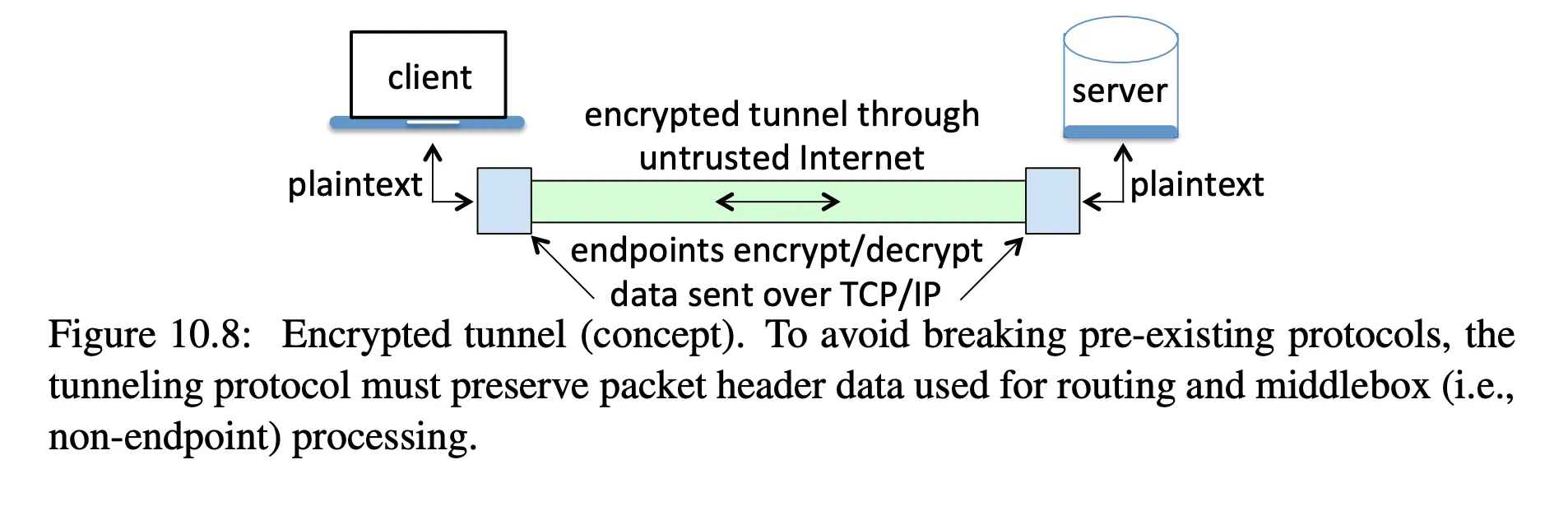
- can use hosts or gateways as endpoints:
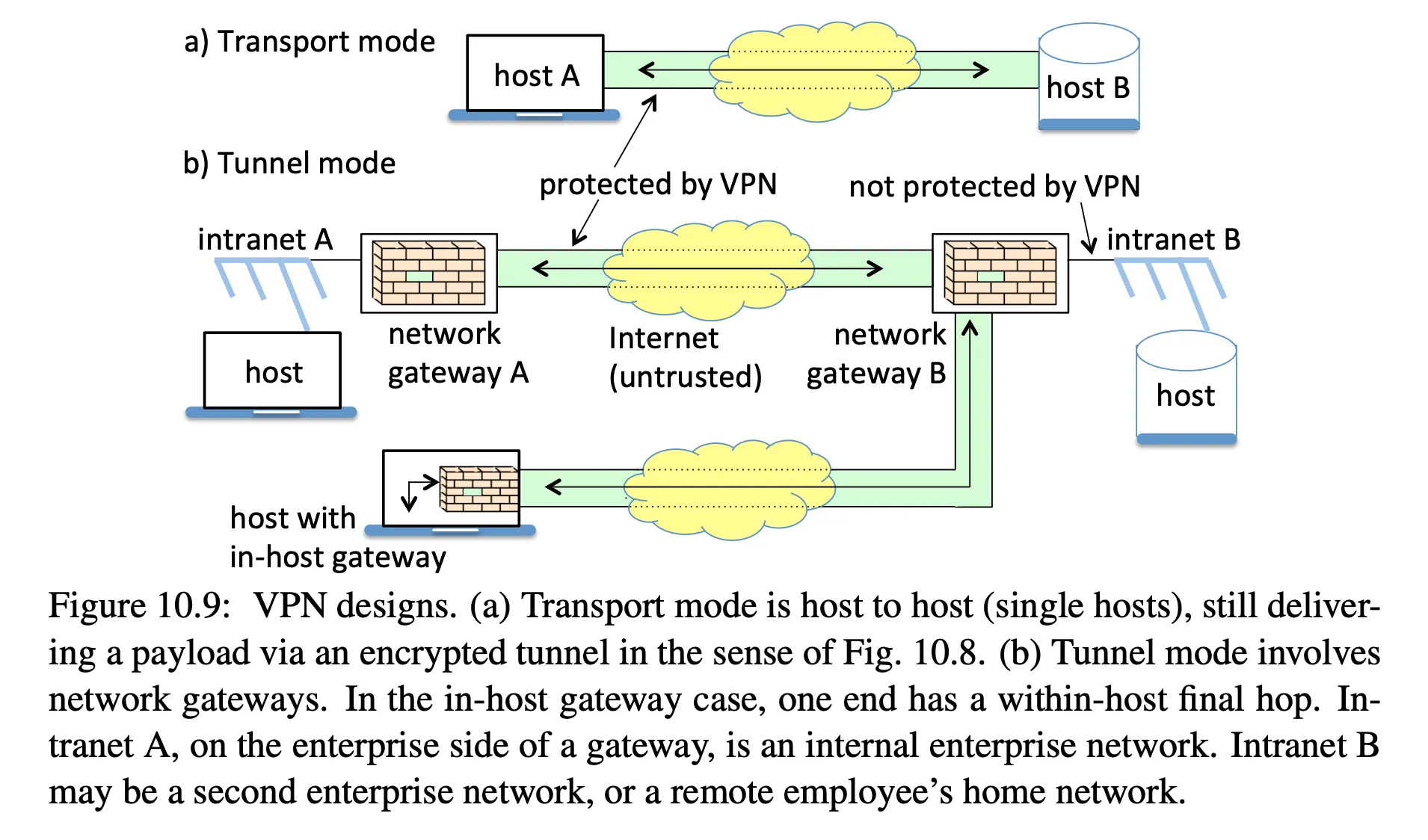
- encrypted tunnels make it difficult for an enterprise to filter malicious content, catch data exfiltration, block unwanted protocols or sites
IPsec
- provide security at the network layer:
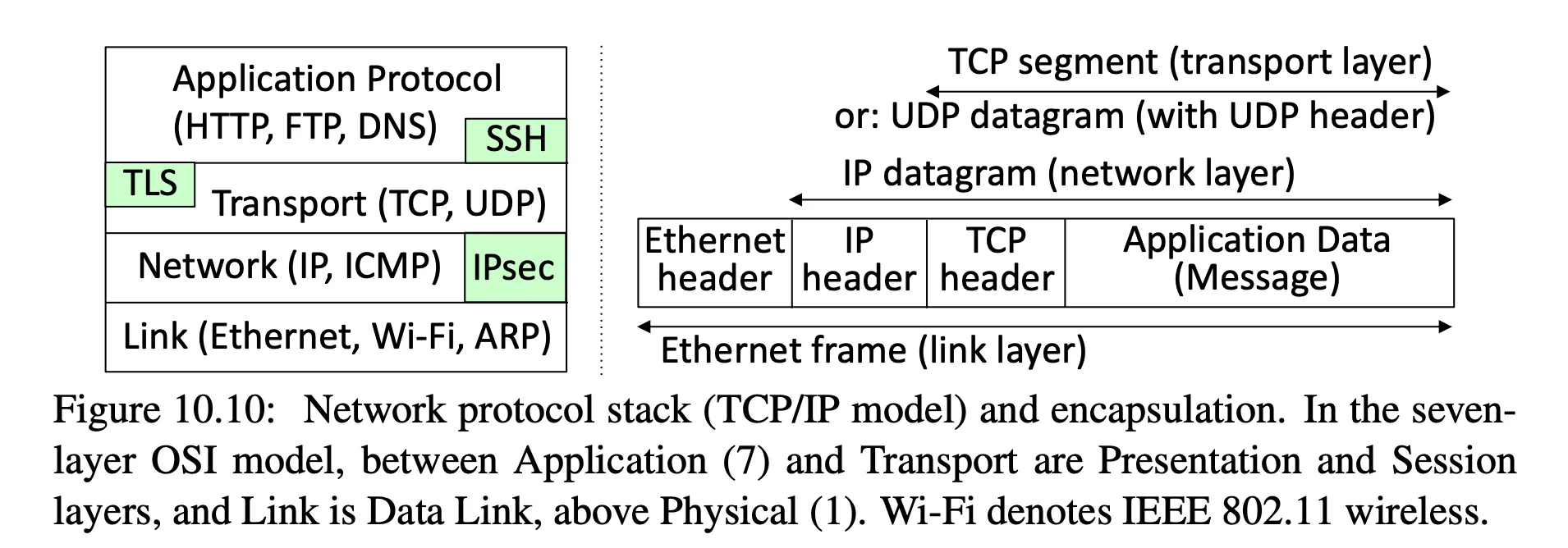
-
used for VPNs
-
Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
- automated key exchange using Diffie-Hellman, plus parameter negotiation
- shared state between endpoints is called a security association (SA) - algorithms, sequence numbers, cryptographic keys
-
Authentication Header (AH)
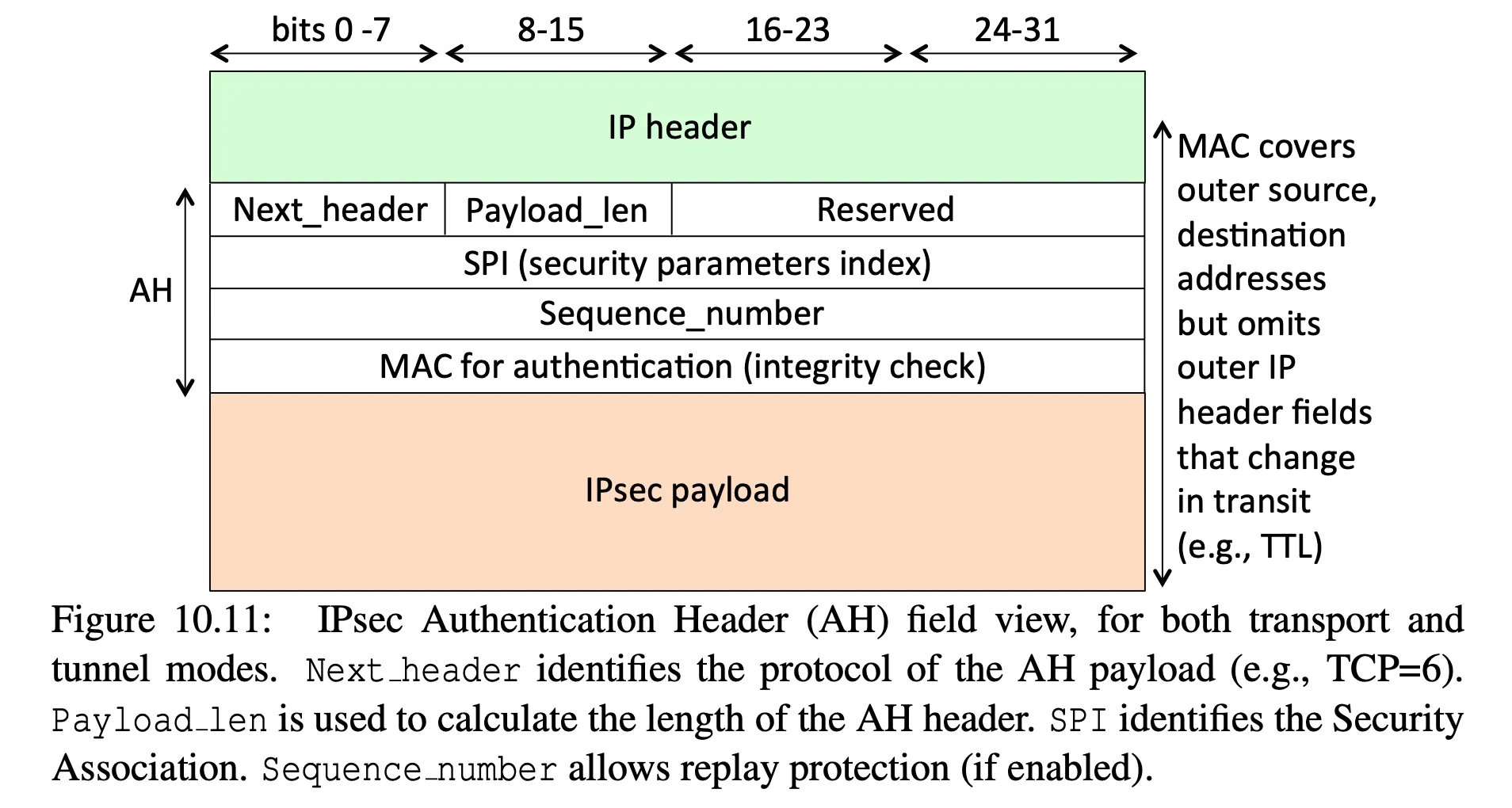
-
used for authentication only (no encryption)
- remember, the IP header contains a Protocol field, this field is set to IPsec, so the receiving router knows that it will next see an AH
- the Next Header field tells what protocol comes next in the payload, e.g. TCP
- the SPI is an index to the SA that was created
-
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
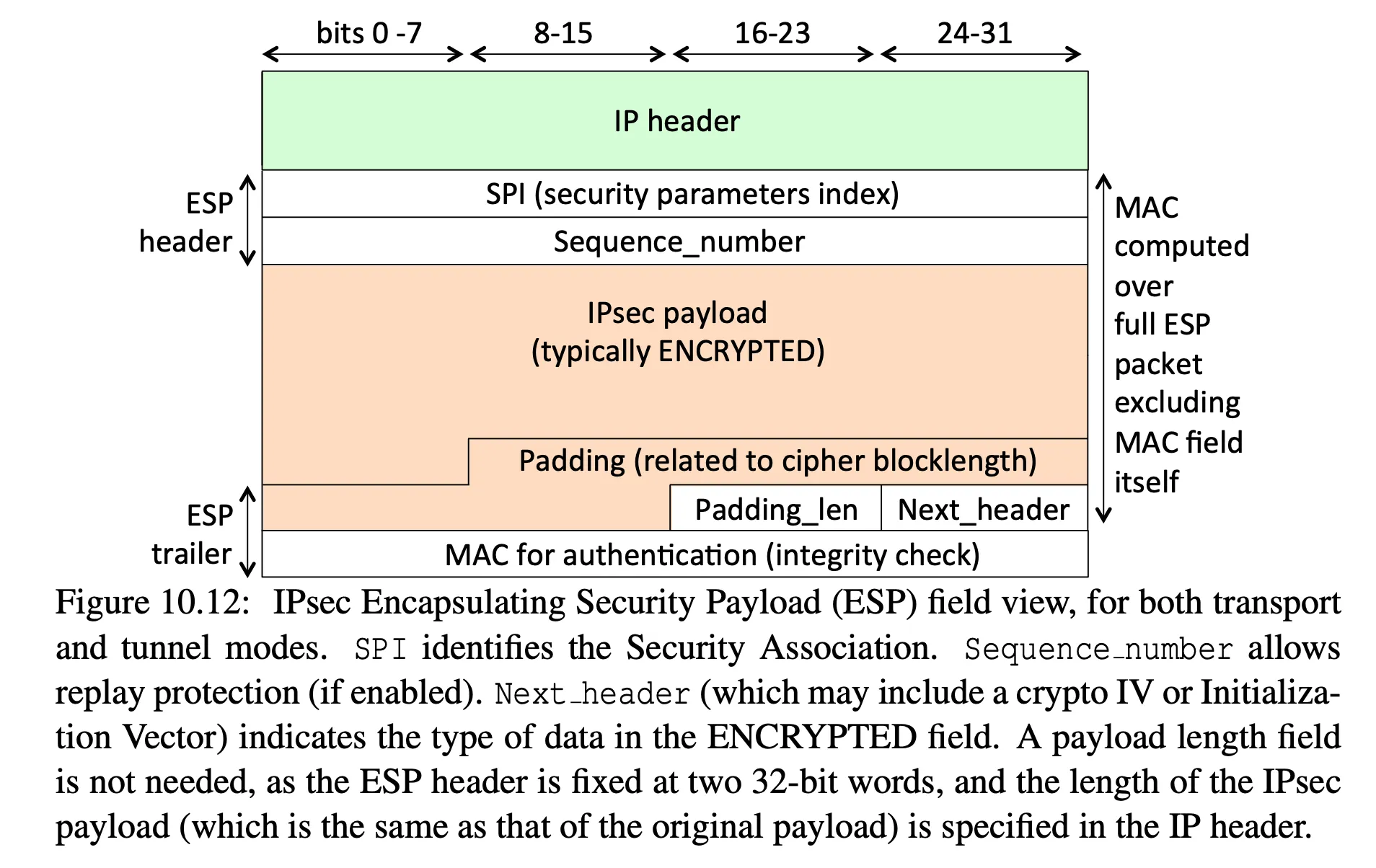
-
used for confidentiality in addition to authentication
- Next Header indicates what type of protocol was encrypted (e.g. TCP or IP)
-
small differences in transport mode vs tunnel mode:
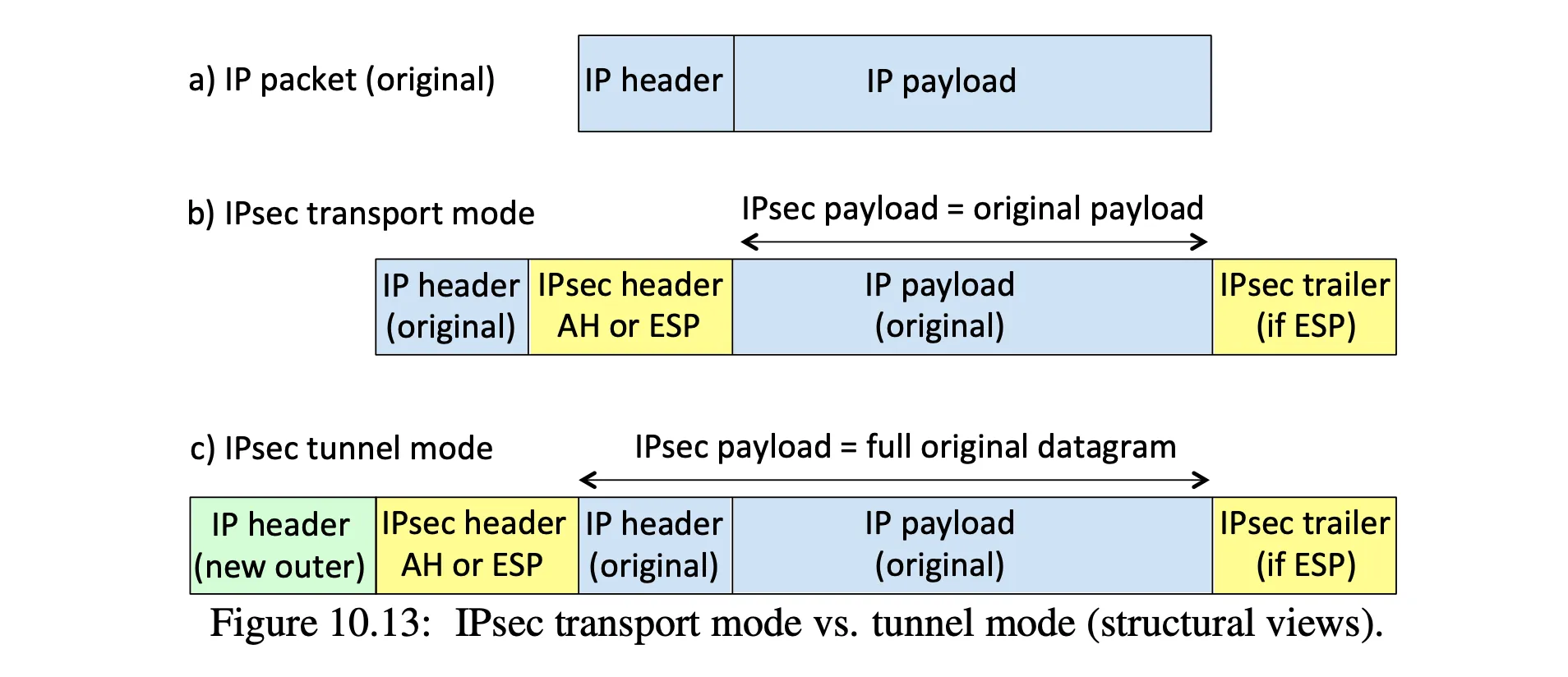
- note that in tunnel mode, the IPsec payload includes an IP header — this is to send the packet to the host after exiting the tunnel, which terminates at a router